Abortion in a Post-Roe America
On June 24th, 2022, at 10:10am, The Supreme Court of the United States ruled in the case Dobbs vs. Jackson Women's Health Organization, that there is no right to an abortion found in the United States Constitution. Supreme Court Justice Samuel Alito in his majority opinion stated boldly and unapologetically: Roe was egregiously wrong.
This Supreme Court Case effectively overturned the Supreme Court cases Roe v. Wade and Doe v. Bolton, which for almost 50 years, allowed the legal slaughter of innocents across the nation, up until the moment of birth, for any reason whatsoever. This result was the murder of over 63,000,000 babies through dismemberment, poisoning, or starvation.
The effect of this decision in the Dobb vs. Jackson Women's Health Organization is that the issue of abortion is now sent back to the people and to their elected representatives. On November 7, 2023 the citizens of Ohio voted by 57% to 43% to enshrine the right to abortion in Ohio's Constitution.
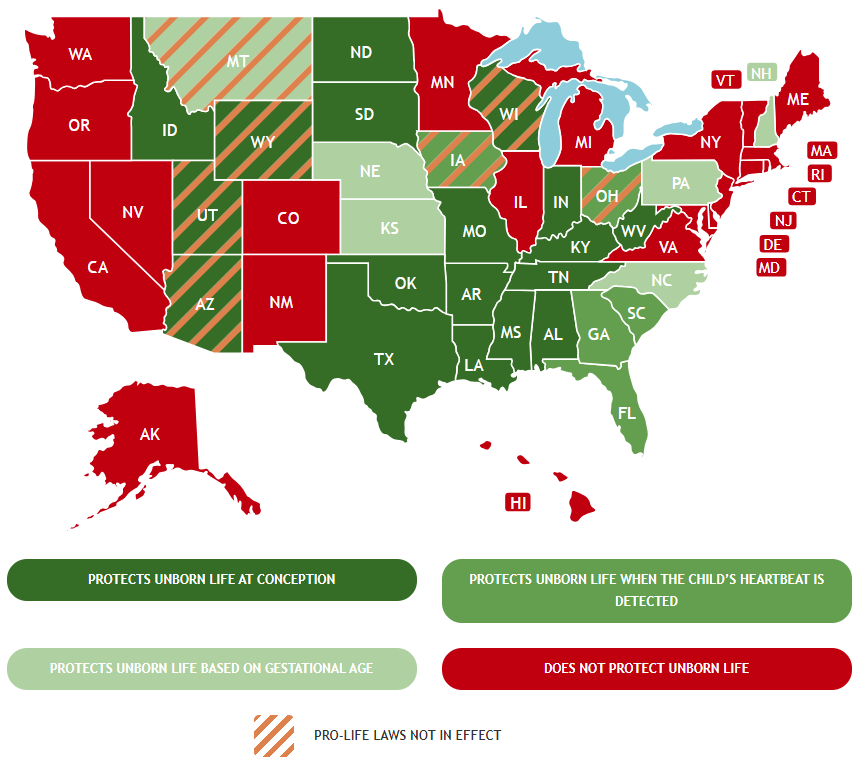
Abortion is Regulated in Varying Degrees in Each State
Ohio's Abortion Laws
Ohio lawmakers passed the heartbeat law in 2019, while Roe v. Wade was still in effect. After the U.S. Supreme Court overturned that decision in June 2022, the law went into effect for just a few months before an Ohio court issued a preliminary injunction against its enforcement. Then, during the 2022 midterm elections, Ohio voters chose to enshrine an amendment into the state’s constitution granting women the legal right to abort their unborn babies. In court proceedings following the passage of that amendment, both sides agreed the central portion of the heartbeat law—which prevents abortionists from killing unborn babies with detectable heartbeats—was unconstitutional.
Abortion Methods
Abortion Pills - First Trimester Medical Abortion
A medical (or chemical) abortion is a non-surgical form of abortion in which the woman takes pills containing Mifepristone (RU-486) and Misoprostol (or Cytotec) to end the life of the baby. This procedure is performed during the first trimester of pregnancy. The drugs are approved by the FDA for use up to ten weeks since the first day of her last menstrual period (LMP).
Aspiration Abortion - First Trimester Suction D&C
A suction, or aspiration, D&C abortion is a procedure in which a suction catheter is inserted into the mother's uterus to extract the preborn baby. Tools are then used to scrape the lining of the uterus to remove any remaining parts. This procedure is performed during the first trimester, typically during five and thirteen weeks LMP (that is five to thirteen weeks after the first day of the woman's last menstrual period).
Dilation & Evacuation Abortion - Second Trimester
A dilation (dilatation) and evacuation abortion, D&E, is a surgical abortion procedure during which an abortionist first dilates the woman's cervix and then uses instruments to dismember and extract the baby from the uterus. The D&E abortion procedure is usually performed between thirteen and twenty-four weeks LMP (that is thirteen to twenty-four weeks after the first day of the woman's last menstrual period).
Induction Abortion - Third Trimester
A third trimester induction abortion is performed at 25 weeks LMP (25 weeks since the first day of the woman's last period) to term. At 25 weeks, a baby is almost fully-developed and is considered viable, meaning he or she could survive outside the womb. For this reason, the abortionist will usually first kill the baby in utero by injecting a substance that causes cardiac arrest, and induces the mother's labor to deliver her baby stillborn.